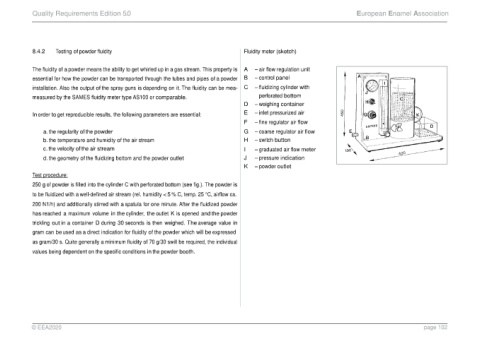
Page 102 - 20250602 EEA QM Edition 6.0
P. 102
Quality Requirements Edition 6.0 European Enamel Association
0.01m Complexion-III-solution: 8.3 Examination of enamels and additives for enamelling
Complexion-III is the disodium salt of ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid
®
®
(mol.wt. 372.1 and available as Titriplex (Merck) and Idranal (Riedel de 8.3.1 Surface tension of enamels
Haen)).
Explanation
Surface tension or interfacial tension is, the surface of a liquid effecting, inwards
directed force. Because of these molecular forces liquids attempt to reduce their
surface. Quite small amounts of liquids endeavour to form a spherical shape. The
higher the surface tension the sooner the ideal spherical shape is attained (Mercury
has a high, water a low surface tension in relation to it). There are substances by which
the surface tension of liquids can be altered.
In the field of enamels and enamelling the surface tension is an object, when the
material changes over from the solid to the liquid state and vice versa. This takes place
while melting as well as while firing the enamel. Porcelain and vitreous enamels with a
high surface tension are aligned during firing towards the metal substrate; those with a
low surface tension towards the surface against air. In fact, the frit manufacturer greatly
attends to this and chooses an oxide composition of the enamel accordingly. Quincke
(1868), Winkelmann and Schott (1884) and others had found relations between surface
tension and the oxide composition of glasses. Dietzel picked up the tasks and obtained
similar correlations to the oxide composition of enamels. In 1942, he published a list of
surface tension factors comprehending a lot of enamel raw materials. The factors have
been established for mN/m percentage by weight. They permit a quite exact
predetermination of the surface tension of enamels. Later on, the list has been enlarged
several times. In the rank described below a small excerpt out of the table of these
factors is given to calculate the surface tension of enamels. The factors relate to 1
percent by weight at times.
-10 - 5.9 0.1 0.8 1.5 3.0 3.4 4.1 4.5 6.2 6.6
MoO Cr O K O B O Na O TiO SiO ZrO CoO/ NiO Al2O MgO
3 3 3 2 2 3 2 2 2 2 3
© EEA2025 page 102